Significance of Pressure groups in Uganda
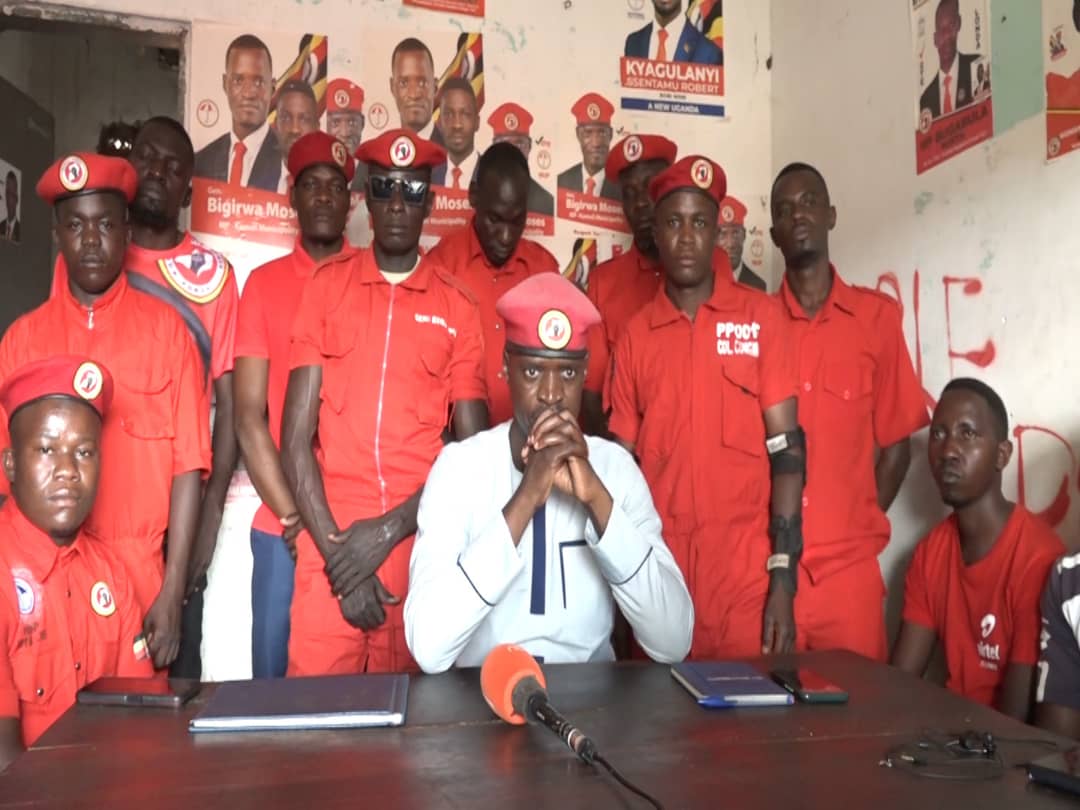

Eastern Revolutionary Platform is the new Pressure group on the political landscape of Uganda.
Under the auspices of National Unity Platform stalwart Moses Bigirwa, the newly formed pressure group was launched today in Jinja.
Keep Reading
According to the brains behind this newly "born baby" it is intended to position Eastern Uganda closer to the National cake.
Uganda is not new to pressure groups, over time there have been numerous pressure groups, though some have caused remarkable change, others suffered a stillbirth.
Notable among those which have shaped the politics of the day include the Reform agenda which birthed Forum for Democratic Change in the early 2000s, Suubi spearheaded by former Katikiro of Buganda Kingdom Mulwanyamuli Ssemwogerere which was used as a political vehicle ahead of 2011 General elections, Activists for Change which was championed by Mathias Mpuuga in 2011, For God and My Country formed by Lord Mayor Erias Lukwago, Truth for Justice by the Late Kato Lubwama, Black Monday Movement of Bishop Niringiye which highlighted mega corruption scandals in the country among.
Here is how Pressure groups can help shape the Political landscape in Uganda.
Political pressure groups in Uganda play a notable role in shaping policy and influencing public opinion, although their significance is tempered by the political landscape and the dominance of the ruling party. Here are several key aspects of their significance:
1. Advocacy and Awareness:
- Pressure groups in Uganda are instrumental in advocating for various social, economic, and political issues. They raise awareness about critical issues such as human rights, environmental protection, and governance reforms.
- Examples include civil society organizations (CSOs) like the Uganda Human Rights Commission and environmental groups like the National Association of Professional Environmentalists (NAPE).
2. Policy Influence:
- Some pressure groups have been able to influence government policies, particularly those related to health, education, and economic reforms. For instance, organizations like the Uganda Debt Network have successfully lobbied for more transparent financial management and debt relief.
3. Public Mobilization:
- Pressure groups often mobilize the public to participate in political processes, such as voting, protesting, or engaging in community discussions. Movements like the Black Monday Movement have engaged citizens in anti-corruption campaigns.
4. Check on Government Power:
- They act as a check on government power by holding authorities accountable. This is particularly crucial in a political environment where the ruling party, the National Resistance Movement (NRM), has a strong hold on power.
5. Challenges and Limitations:
- Despite their efforts, pressure groups in Uganda face significant challenges, including political repression, legal restrictions, and limited funding. The government has sometimes responded to their activities with intimidation and harassment.
- The Public Order Management Act (POMA) has been used to restrict public gatherings and protests, limiting the ability of pressure groups to operate freely.
6. International Support:
- Many Ugandan pressure groups receive support from international NGOs and donors, which helps them sustain their activities and amplify their voices. This international backing can sometimes protect them from domestic repression.
In summary, political pressure groups in Uganda are significant in promoting advocacy, influencing policy, mobilizing the public, and providing a check on government power. However, their impact is constrained by political repression and legal restrictions, making their operating environment challenging.